Jun P. Espina 11 min read
Updated on June 25th, 2022
The 7 Benefits of Blueberries When Consumed Daily
The benefits of blueberries may include degenerative health issues like heart diseases, metabolic syndrome (e.g. diabetes, high blood pressure, etc.), impaired immune function, neurological (Alzheimer’s, dementia) disorders, poor cognitive function (memory loss), fatigue, eyesight issues, obesity, and cancer.
Benefits of Blueberries
Blueberries are known to contain potent phytonutrients (plant chemicals) with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and other properties essential in boosting our DNA and immune health. Powerful anthocyanins represent the major red, purple, and violet pigment in many plants and fruits and the purplish deep-blue skin in blueberries.
Wrote Wilhelmina Kalt, et al. on the benefits of Blueberries: “Blueberries contain a large number of phytochemicals, including abundant anthocyanin pigments. Of their various phytochemicals, anthocyanins probably make the greatest impact on blueberry health functionality. Epidemiological studies associate regular, moderate intake of blueberries and/or anthocyanins with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, death, and type 2 diabetes, and with improved weight maintenance and neuroprotection.” [1]
The Benefits of Blueberries Cover Their Health Role in Chronic Diseases

Luyao Ma, Zhenghai Sun, et al. also confirmed that “Blueberry is rich in flavonoids (mainly anthocyanidins), polyphenols (procyanidin), phenolic acids, pyruvic acid, chlorogenic acid, and others, which have anticancer, anti-obesity, prevent degenerative diseases, anti-inflammation, protective properties for vision and liver, prevent heart diseases, antidiabetes, improve brain function, protective lung properties, strong bones, enhance immunity, prevent cardiovascular diseases, and improve cognitive decline. The anthocyanins and polyphenols in blueberry are major functional ingredients for preventive chronic disease. These results support findings that blueberry may be one of the best functional fruits, and further reveals the mechanisms of anthocyanins and polyphenols in the health role of blueberry for chronic disease.” [Emphasis supplied.] [2]
Table 1: Illustrates the Functional Ingredients for Preventive Chronic Disease in Blueberry.
| Chronic Disease | Functional Components |
|---|---|
| Anticancer | Anthocyanins, phenolic acids, pyruvic acid, pterostilbene |
| Anti-obesity | Anthocyanins, polyphenols |
| Prevent degenerative diseases | Anthocyanins, chlorogenic acid, polyphenols |
| Anti-inflammation | Anthocyanins, phenolic acids, flavonoids |
| Protective vision | Anthocyanins, polyphenols |
| Protective liver | Anthocyanins, polyphenols |
| Prevent heart diseases | Anthocyanins, procyanidin, polyphenols |
| Antidiabetes | Anthocyanins, polyphenols |
| Improve brain | Anthocyanins, phenolics |
| Protective lung | Anthocyanins |
| Strong bones | Anthocyanins |
| Enhance immunity | Polysaccharide, polyphenols |
| Prevent cardiovascular diseases (heart and blood vessels) | Phenolic acids, flavonoid |
| Improve cognitive decline | Polyphenols |
[▸ Source of Table 1]
1. May Help Keep Your Heart Healthy
We find in Table 1 that the functional ingredients in blueberry for heart disease are anthocyanins, procyanidin, polyphenols, and cardiovascular diseases (heart disease and those issues affecting the blood vessels), phenolic acids, and flavonoids. These nutrients and phytochemicals found in blueberries are understood in layman’s terms easily if we factor in polyphenols—the biggest group of phytochemicals—contained in this superfood.
Polyphenols are antioxidants phytochemicals from which flavonoids are a member of the polyphenol family, and anthocyanin, a type of flavonoids.
Polyphenols give the plant color, taste, and protective layers against diseases, and pests, and “help protect them in many different ways.” The four main types of polyphenols are (1) lignans (e.g. seeds); (2) stilbenes (e.g. dark chocolate, red wine); (3) phenolic acids (e.g. cinnamon, clove, oregano); and flavonoids (e.g. wine, green tea, many fruits and vegetables). [3]
One study shows the activities of blueberries in reducing the risk elements for cardiovascular disease. A cup of these fruits (or 150 grams) daily proves to work by up to 15 percent. [4]
• The Benefits of Blueberries Come from Different Nutrients and Phytochemicals.
1. Flavonoids. Berries are rich in polyphenols. One of the two general classes of polyphenols (out of over 8000 types identified) is flavonoids. The other major class is phenolic acids. [5] They are “involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation, various environmental pollutants, and pathogens.” [6] Flavonoids are a “very diverse group of phytonutrients.” Anthocyanins are a subclass of Blueberry flavonoids that have a ton of health benefits for human beings.
2. Anthocyanins. “Anthocyanin isolates and anthocyanin-rich mixtures of bioflavonoids” and the activities of polyphenols work together to potentiate blueberry’s health benefits. Anthocyanins have antioxidant, anti-viral, and other properties. [7, 8]
The benefits of blueberry anthocyanins “include anticancer, anti-obesity, prevent degenerative diseases, anti-inflammation, protective vision, protective liver, prevent heart diseases, antidiabetes, improve brain, and protective lung.” [9]
• The Benefits of Blueberries Come from Very Potent Antioxidants.
1. Free Radical Scavengers. Anthocyanins are used in a variety of nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, medicinal and cosmetic applications. These plant compounds are subdivided into different subgroups, which are: “flavones, flavonols, flavanones, flavanonols, flavanols or catechins, anthocyanins and chalcones.” [10] Their free radical scavenging abilities qualify anthocyanins as “some of the strongest antioxidants.” [11] Blueberries contain anthocyanins richly.
2. 365 Different Anthocyanins. Wrote Dr. Axe: “Anthocyanins are a family of powerful antioxidants that fight the effects of aging and oxidative stress. To date, more than 635 different anthocyanins have been identified.” [12]
2. Blueberries are Proven to Support Eye Health

Eye Vitamin. Visual acuity may be improved by eating blueberries or their capsulized concentrates. Anthocyanin pigments prove to “enhance night vision or overall vision.” [13] Blueberry is second only to cloudberry for having the highest total carotenoid content among berries. “All berries had lutein but it was a predominant carotenoid in blueberry,” which is an eye vitamin. [14] Lutein and zeaxanthin carotenoids are eye-nourishing phytonutrients that reduce eye fatigue and improve night vision. The coaction of the carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin and the flavonoids anthocyanins proves blueberries’ health-giving benefits for eye sharpness.
3. May Lower the Risk of Cancer
Colon Cancer. Blueberries contain the highest content of anthocyanidins (a subclass of flavonoids), and research shows these “Berry phenolics have protective effects in relation to colon carcinogenesis.” [15] The powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of blueberries elicited a reduction, according to research, in intestinal inflammation and colon tumorigenesis. The anthocyanins of bilberry reduced the symptom of adenomatous polyposis, “a condition characterized by multiple intestinal polyps potentially developing to carcinomas.” [16] Blueberry has higher anthocyanins than bilberry. [17]
Effective Against Carcinogenesis. Mary Ann Lila wrote that “anthocyanins have demonstrated marked ability to reduce cancer cell proliferation and to inhibit tumor formation . . . interfere with the process of carcinogenesis . . . inhibit tumorigenesis by blocking activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. In other research, fruit extracts with significant anthocyanin concentrations proved to be effective against various stages of carcinogenesis.” [18]
Berries chemopreventive and therapeutic responses against cancer through the following mechanisms and modes of action. [19]
- Anti-oxidative action (Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) sequestration).
- Effects on enzymes of phase-I and -II.
- Cell-cycle arrest.
- Induce apoptosis (cell suicide).
- Anti-proliferation/Anti-survival of cancer cells.
- Anti-inflammatory action (stop cell inflammation).
- Anti-angiogenesis (block new blood vessels for cancerous tissues).
- Metastasis inhibition (induce cancer cell dormancy).
- Cell adhesion and movement inhibition (check the spread of cancer).
How Do Berries Interrupt the Inflammation/Oxidative Stress Cycle?
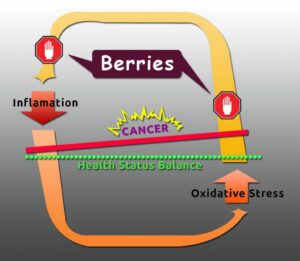
The Benefits of Blueberries May Include the Reduction of the Risk of Breast Cancer
Fight Breast Cancer. A recent study conducted in New Zealand proves that breast cancer’s cellular abnormalities could have been avoided or at least minimized with regular consumption of these fruits. “Women might be able to reduce the risk of breast cancer by eating more blueberries, according to a New Zealand research.” Wrote Janyawat Vuthijumnonk, “Blueberries contain phytochemicals called anthocyanins, which may be responsible for the health benefits of blueberries. They reduce free radicals in our system, decrease new blood vessel formation and increase the number of beneficial bacteria—all elements which help in the fight against breast cancer.” [20]
https://www.standardmedia.co.ke/health/health-science/article/2000201652/researchers-say-a-blueberry-diet-can-lower-breast-cancer-risk
More Research Needed. Laboratory studies show the many phytochemicals, the powerful antioxidant compounds, and the anthocyanins stuffing blueberries that have anticancer effects and the potential for DNA damage protection. Blueberries have the properties to suppress inflammatory and oxidative processes. They inhibit cancer cell proliferation and cause apoptosis in cancer cells. Oxidative stress which results in oxidative DNA damage marks the development of different cancers. More studies are needed, though, to understand the complexities of blueberry’s role in cancer prevention.
4. May Help Control Blood Pressure
“Daily blueberry consumption may reduce blood pressure and arterial stiffness, which may be due, in part, to increased nitric oxide production.” [21]
“Accumulating evidence indicate that blueberries have anti-hypertensive properties, which may be mainly due to its rich polyphenol content and their high antioxidant capacity.” [22]
“Daily blueberry consumption may reduce blood pressure and arterial stiffness, which may be due, in part, to increased nitric oxide production.” [23]
⚙ ⚙ ⚙
Causes of Hypertension
• Smoking
• Being overweight or obese
• Lack of physical activity
• Too much salt in the diet
• Too much alcohol consumption (more than 1 to 2 drinks per day)
• Stress
• Older age
• Genetics
• Family history of high blood pressure
• Chronic kidney disease
• Adrenal and thyroid disorders
• Sleep apnea
hypertension two hours after consuming blueberry drinks. Researchers saw improvement in endothelial function, “a key factor in blood clotting and blood pressure regulation.”
5. Blueberries May Help Obesity and Diabetes
One cause of obesity is the lack of a healthy gut microbiome. Good gut bacteria feed on prebiotics from the soluble fibers we ate. Chia seeds and flaxseed are prebiotics (they feed our gut microbiome) better than any probiotic supplement given the possibility of dead lactobacillus acidophilus inside its capsules. The second cause is excess consumption of sugary food like grains (bread), soda, and fruit drinks. Third is stress, lack of exercise, no restful sleep (stage 4) during the night, and sedentary life. One author said: “Move or Die.”
Study shows that “Blueberry phytochemicals may affect gastrointestinal microflora and contribute to host health. . .. In a study with high-fat–fed rats, blueberry intake moderated the negative effects of the high-fat diet on inflammation and insulin signaling and also led to modification of the gut microbiota.” [24]
The Benefits of Blueberries May Include the Lowering of the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
“Blueberries are a rich source of polyphenols, which include anthocyanin bioactive compounds. Epidemiological evidence indicates that incorporating blueberries into the diet may lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes (T2DM). These findings are supported by pre-clinical and clinical studies that have shown improvements in insulin resistance (i.e., increased insulin sensitivity) after obese and insulin-resistant rodents or humans consumed blueberries.” [25]
The most obese country, according to WHO in 2020, is Nauro (10,000 population near Papua New Guinea) and the problem is an unhealthy diet and sedentary lifestyle. Wrote Jannette Aguirre: “The obesity and overweight problem found in Nauru may be because of the lack of proper nutrition in Nauruan’s diets. Many of their diets consist of white rice, instant noodles, imported Westernized foods and soda with very little fruits and vegetables.” [27] The mention of “Westernized foods” (plus the American obesity epidemic!) speaks volumes.
6. May Reduce Cognitive Decline
In Table 1, we pointed out the polyphenols (the family of flavonoids and anthocyanins) in blueberries as one antioxidant phytochemical that helps boost cognitive function. The declining memory retention that we experienced as we age may be curbed by eating this super fruit regularly. It is a part of the benefits of blueberries.
“Blueberries,” reported Robert Krikorian, et al., “contain polyphenolic compounds, most prominently anthocyanins, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. In addition, anthocyanins have been associated with increased neuronal signaling in brain centers mediating memory function as well as improved glucose disposal, benefits that would be expected to mitigate neurodegeneration. We investigated the effects of daily consumption of wild blueberry juice in a sample of nine older adults with early memory changes. At 12 weeks, we observed improved paired associate learning (p = 0.009) and word list recall (p = 0.04). In addition, there were trends suggesting reduced depressive symptoms (p = 0.08) and lower glucose levels (p = 0.10).” [28]
7. May Help Boost the Immune System
In Table 1, we wrote about the “functional ingredients” that mark the benefits of blueberries. The natural antioxidant properties of these super fruits (namely: the polyphenols, flavonoids, anthocyanins, and their related synergistic nutrients and chemical compounds) can stabilize harmful molecules in the body known as free radicals (or molecules having unpaired electrons).
Free radicals cause illness and aging.
These free radicals are abnormal cells (highly reactive and unstable molecules) that damage normal cells in the body. Inhalation of toxins like tobacco smoke, for example, can trigger a free-radical attack on your healthy cells (or those having paired electrons). Consuming blueberries regularly may help subdue free-radical attacks (or the “stealing” of electrons from healthy cells).
The Benefits of Blueberries Hinged on the Highly Powerful Antioxidants They Contain
Eating antioxidant-rich vegetables and fruits like blueberries is essential in extending one’s healthspan.
“Exposure to UV light, cigarette smoke, and other environmental pollutants also increases the body’s free radical burden. The harmful activities of free radicals are associated with damage to membranes, enzymes, and DNA. The ability of antioxidants to destroy free radicals protects the structural integrity of cells and tissues.” [30]
⚙ ⚙ ⚙
DISCLAIMER
THIS WEBSITE DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE.
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Notes
Ref. Numbers 1-10
1) Wilhelmina Kalt, et al. “Recent Research on the Health Benefits of Blueberries
and Their Anthocyanins.” National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31329250/ (accessed June 24, 2022).
2) Luyao Ma, et al. “Molecular Mechanism and Health Role of Functional Ingredients in Blueberry for Chronic Disease in Human Beings.” National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6164568/ (accessed June 24, 2022).
3) Gundry MD Team. “Break Down of Polyphenols: What Are They & What Do They Do?.” GUNDRY MD. https://gundrymd.com/what-are-polyphenols/ (accessed June 24, 2022).
4) University of East Anglia. “Eating blueberries every day improves heart health.” ScienceDaily. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/05/190530101221.htm (accessed June 24, 2022).
5) Manuwar Abbas, et al. “Natural polyphenols: An overview.” Taylor & Francis Online. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10942912.2016.1220393 (accessed June 24, 2022).
6) Mary Ann Lila. “Anthocyanins and Human Health: An In Vitro Investigative Approach.” PubMed Central. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1082894/ (accessed June 24, 2022).
7) Correa-Betanzo J, et al. “Stability and biological activity of wild blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium) polyphenols during simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion.” PubMed Central. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25038707 (accessed June 24, 2022).
8) Cathy Wong. “What Are Anthocyanins?” verywellhealth. https://www.verywellhealth.com/the-scoop-on-anthocyanins-89522 (accessed June 24, 2022).
9) Luyao Ma. Ibid.
10) A. N. Panche, et al. “Flavonoids: an overview.” PubMed Central. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5465813/ (accessed June 24, 2022).
Ref. Numbers 11-20
11) Hock Eng Khoo, et al. “Molecular Mechanism and Health Role of Functional Ingredients in Blueberry for Chronic Disease in Human Beings.” PubMed Central. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6164568/ (accessed June 24, 2022).
12) Jillian Levy, CHHC. “Anthocyanin Benefits the Brain, Eyes & Immune System.” Dr. Axe https://draxe.com/nutrition/anthocyanin/ (accessed June 24, 2022).
13) Mary Ann Lila. Ibid.
14) Katya A Lashmanova, et al. “Northern berries as a source of carotenoids.” ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221716537_Northern_berries_as_a_source_of_carotenoids (accessed June 25, 2022).
15) Aleksandra S. Kristo, et al. “Protective Role of Dietary Berries in Cancer.” PubMed Central. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5187535/ (accessed June 25, 2022).
16) Aleksandra S. Kristo, et al. Ibid.
17) Deividas Burdulis, et al. “Comparative study of anthocyanin composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activity in bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) and blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) fruits.” National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19702172 (accessed June 25, 2022).
18) Mary Ann Lila. Ibid.
19) Aleksandra S. Kristo, et al. Ibid.
20) Xinhua. “Researchers say a blueberry diet can lower breast cancer risk.” The Standard. https://www.standardmedia.co.ke/health/health-science/article/2000201652/researchers-say-a-blueberry-diet-can-lower-breast-cancer-risk (accessed June 25, 2022).
Ref. Numbers 21-30
21) Sarah A Johnson, et al. “Daily blueberry consumption improves blood pressure and arterial stiffness in postmenopausal women with pre- and stage 1-hypertension: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.” National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25578927/ (accessed June 25, 2022).
22) Rami S Najjar et al. “Blueberry Polyphenols Increase Nitric Oxide and Attenuate Angiotensin II-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Signaling in Human Aortic Endothelial Cells.” National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35453301/ (accessed June 25, 2022).
23) Johnson SA, Figueroa A, et al. “Lower Blood Pressure with Blueberries.” WorldHealth.Net. https://www.worldhealth.net/news/lower-blood-pressure-blueberries/ (accessed June 25, 2022).
24) Wilhelmina Kalt, et al. Ibid.
25) April J Stull. “Blueberries’ Impact on Insulin Resistance and Glucose Intolerance.” National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5187542/ (accessed June 25, 2022).
26) Amanda Penn. “Why Are Americans So Fat? 4 Reasons You Haven’t Considered.” SHORTFORM. https://www.shortform.com/blog/why-are-americans-so-fat/ (accessed June 25, 2022).
27) Jannette Aguirre. “5 FACTS ABOUT NAURU’S OVERWEIGHT HEALTH ISSUE.” The BorGen Project. https://borgenproject.org/5-facts-about-naurus-overweight-health-issue/ (accessed June 25, 2022).
28) Robert Krikorian, et al.. “Blueberry Supplementation Improves Memory in Older Adults.” National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2850944/ (accessed June 25, 2022).
29) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “The Effects of Diabetes on the Brain.” CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/features/diabetes-and-your-brain.html (accessed June 25, 2022).
30) A Bendich. “Physiological role of antioxidants in the immune system.” National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8227682/ (accessed June 25, 2022).


